In a global economy, everything is negotiated, traded and recorded in silos. Every enterprise has their softwares, databases, and systems to validate, record and retrieve information. They use primitive technology for communication with outside parties, like emails, excel sheets, invoices, and POs. Those third parties also use manual teams to again digitize them in own systems for using that information.
Here’s our comprehensive analysis…
Potential Problems Due to this Model:
- A considerable amount is unstructured and unactionable in communication
- Lost in Translation
- Chances of Skipping interaction
- Manual digitization by all parties after receiving copies
- Byzantine General Problem (No trust of information)
- Email/Interactions don’t become generally enforceable law.
- Expected time of Delivery and promised quality is compromised due to clear communication.
- Every third party’s company is a black box for the enterprise. It is just based on expensive agreements, and good faith business is running.
- All data and commitment supplied by third parties have financial incentives involved. So the probability of over-committing and under-performing is very high.
- No single version of the truth with internal teams, enterprise level or third-party levels.
Challenges of Adopting Blockchain in Enterprises Data
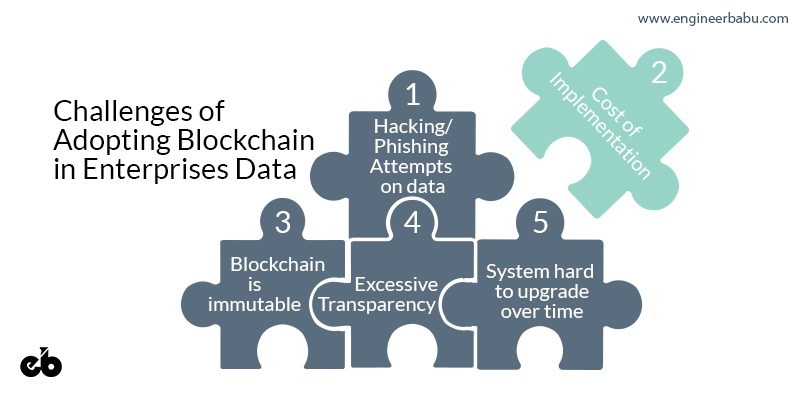
- Hacking/Phishing Attempts to System and Data
- Encrypted Data might get decrypted after a few years. Due increase in Computing power of solve keys. Quantum computer posses that threat.
- Supply chain stakeholders business data, employee data, and systems are costly. It will have more probability and chances of attack due to cost/benefits from Competitors/Hackers.
- Supply chain stakeholders and ex-Employees can have threats to Blockchain System. Due to consensus and web access during the time of transition. Blocks inside Blockchain are immutable.
- The consistency of System is based on permission and consensus. It is a dynamic model, which can change and evolve in the supply chain network.
- Stores and Brands will have more transparency and information of chain. They might use this information for reducing the profit margin for other stakeholders.
- Planning in every phase should be strong and future ready. Otherwise, it will become obsolete, cumbersome, costly and time consuming to upgrade.
- Upgrades are tough in blockchain. Due to immutability and every new version will have different Data Block Format. It will make the system hard to upgrade over time.
- Fraud/Risk/Push/Gaps exploited by Stakeholders
Few Solutions:
- Selecting Private Blockchain with strong fundamental architecture.
- We will select private blockchain solution which is resilient, data critical for time, no loss to business and trade secret.
- Selection of private blockchain solution should be focused on big three companies. IBM, Microsoft, and Amazon. We need upgrades and security updates.
- Small companies might shut down or have problems in securing the Blockchain database. The process of upgrading is highly required by platform.
- Hacking, decryption and security breach should not affect trade secrets.
- A pseudo naming convention for all stakeholders, order ids, item names and details with encryption and permission-based access should be used.
- Consensus Model should be applied for adding, editing and stage crossing blocks. Consensus parties should be decided based on the hierarchy of parties and decision permission for that block.
- Every Consensus Blocks will always be controlled by stakeholders 2-5 employees per Stage. We will not give control to Suppliers to edit expected time Deliver (ETD) without Manufacturer permission or Manufacturer to edit expected time deliver (ETD) without Brand Approval.
- Controlling Access, Permission for reading, writing, and editing based on need-to-know and involvement is essential.
- In case of an upgrade, the code should have a version number in each block to understand the algorithm and study those blocks. At a level of inconsistency, we need flags and systems.
- Upgrades will always be deployed at network start genesis chain start level, which is order from store or brand. If there are old orders, which have not reached their conclusion (Delivery). Then those chains will follow old function in data block process flow. (It is a complicated process, and creative ideas are needed.)
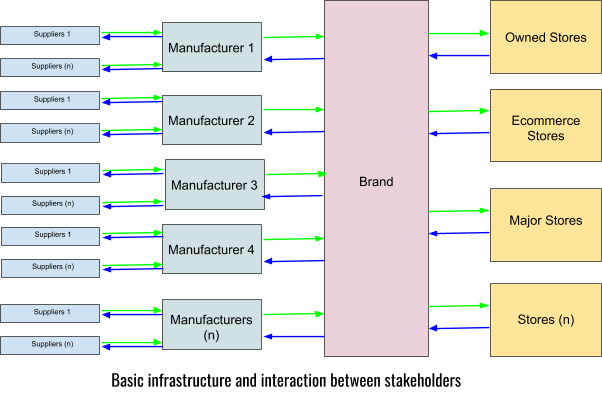
Basic Process of Supply Chain
Supply Chain in 2025:
- Stakeholders have to open data to work with each other. Stakeholders like suppliers, manufacturers, shipping companies, brands, and stores. It will create a chain of trust and confidence to do business together.
- Suppliers have to open current raw material and finished good inventory to Manufacturers before purchasing order. It will be based on a need-to-know basis for the manufacturer. The supplier will need bank balance assurance from Manufacturers with all future commitment included.
- Manufacturers have to open production line data, human resources data, the condition of human resources, waste management and the actual time of delivery updates at a real time. Manufacturers will need bank balance assurance from brands with all future commitment included.
- Shipping companies have to open capability and capacity data for better booking. They have to provide real-time data of ship/air positions to supply chain. Shipping companies will need bank balance assurance from parties.
- Brands have to open their purchasing power to make manufacturer assured of payments and faster delivery. They expect same from stores.
- Stores have to open data of user behavior with brands in the deeper level like style trail room visits, a style which has more hand touch and sales graph with user profiling. Brands will deliver more information about ad campaign performance, digital eCommerce performance, and planning process.
- Once this data will open, and a new consensus model will evolve at every stage. Then smart contracts will start to remodel in the supply chain industry. e.g, If you deliver on this date automatically, payment will be made on this date, and if you delay by one day without approval, 0.1% will be deducted off the invoice amount as penalty.
- We will move away from paper contracts, and configurable contracts will evolve in the industry with standard codes. Both parties will verify smart contract code and accept. Once accepted it would be implemented in that stage or at purchasing order.
- It has to record a chain of events by a machine to machine, machine to software and software to software interaction. Humans will interact with natural language, and it has to be converted to actionable items, event recording, stage shifting and consent given/not given the model.
- Consensus Model will be based on the Byzantine General problem. We need to get consent from parties involved to change stage. It is also based on rights they will have for voting in stage transfer or not. e.g, Change of date for the expected time of delivery cannot be done, supplier. The manufacturer can only do it with internal teams consent.
Just Imagine, all this data is shared between companies and third parties with machines, ERP softwares, IoT devices, emails, excels sheets, CCTV and images with a need-to-know basis and preserving trade secrets.
Currently, only blockchain can solve the problem of integrating all this data with consensus between parties and immutability for fraud-proof.
Basic guidelines for Designing
This solution list of the foundation of product development. We have to achieve all the mentioned points in various phases of the project.
- Truth is Key to unlock the potential of organizations
- One version of Truth
- Truth is defined by the maximum ability to know reality. Rest is subjective truth, stories and the second version of truth.
- Supplier accepting the expected date of delivery (ETD) should have double confirmation System. So we have a very sure commitment from Suppliers.
- We should never apply double confirmation for Brand. They are a prime source of truth for Manufacturing companies. Editing of ETD rights should be always allowed to Brand.
- One version of Truth can be derived only by knowing chain of events and consensus of that event with timestamp stored with immutability.
- Every interaction with stakeholders, internal teams, top management is event. It should be tracked and inserted in chain.
- Few events will require double confirmation before entering in the chain. As events are immutable. We need them to be double confirmed with the event when the stage is crossed from one set to another. e.g Supplier shipped material from China.
- Extracting one version of Truth/Chain incase of any conflict with Store/Brand/Manufacturer/Supplier/Internal Team
- Segregation of Information based on necessity.
- Cost is sensitive data but time is critical performance data, which needs to free flow from Store/Brand/Manufacturer/Supplier/Internal Team.
- Two level of data encapsulation and security is needed when we will insert supplier, manufacturer, Brand, Shipping and Stores data in Blockchain.
- Non-Sensitive information in Blockchain.
- We will never insert Encrypted or Unencrypted sensitive information about price/cost in Blockchain. (Cryptography can be broken with Quantum Computer or Future technology or Hacking or Platform Bug of Blockchain. We should never be vulnerable to that hacking in future. It can be cracked after 20 years when technology is ready. It will become an embarrassing situation for stakeholders. Precaution is better with Blockchain)
- Time ETD is non-sensitive information but within the ecosystem of stakeholders.
- Information Distribution in real time
- We have only Information Asset within the supply chain network. We need this to free flow for best results. Information like time, raw material, ETD for order and time-sensitive information within the network. ETD and ETA should be strict and enforced across teams and need to know basis.
- Top management should receive focused information to all stakeholders.
- Alert system for better knowledge and monitoring (Email Focused)
- Open/Reply/Forwarding Emails from stakeholders as Analytics and Knowledge.
- Agile and Actionable information to find gaps before it is too late.
- Timeline strict project should have special considerations in System with more strict Alert systems.
- Stakeholders with track record is important. We can plan penalties for not responding and delaying in system.
- Department/Head/Employees agility should be tracked and rewarded.
- Top management should be kept in driving seat rather than receiving information from the hierarchy.
- Predictive Logic: Foundation of this logic will be written on stakeholders past record of supplied orders. Assuming we have low ranking suppliers (low ranking means delaying inventory suppliers) in particular brands. Then we should focus on them as well as orders.
- System of every order with supplier/manufacturer past record can give you likelihood of order completion on time. It is probability theorem but effective for triggering danger orders. It will need machine learning on past data and conversation.
Mode of Communication of Stakeholders
Store, Brand, Manufacturer, Supplier, and Shipping companies.
- Email(Heavy used system with maximum inefficiency)
- Image Proof/CCTV footage(Applied to all stakeholders.)
- Excel Sheet (Non-standard Formats and highly different across emails and ecosystem.)
- RFID(Complicated and different implementation by each stakeholder. Data planning is needed for it.)
- ERP(Structured Data and System. Sharing them on blockchain will be key.)
- IOT and Custom Devices(Monitoring, Analysing, Measuring, Access control data can also be inserted in blockchain to derive chain of events.)
- Open APIs for Shipping companies and other stakeholders (It is entirely dependent on stakeholders implementation. Eg. Fedex Tracking API is easy. But shipping companies is tough.)
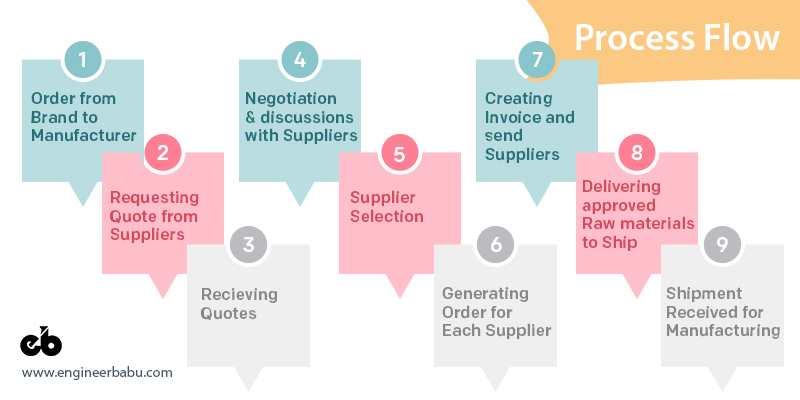
Process Flow
- Order from Brand to Manufacturer
- Requesting Quote from Suppliers
- Receiving Quotes
- Negotiation and discussions for best ETD and Price with Suppliers
- Suppliers Selection
- Generating order for each supplier.
- Account team will create Invoice and send Suppliers.
- Supplier delivers Quantity and Quality approved raw materials to shipping companies.
- Shipping received for manufacturing.
Planning Process for development
- Methods for Interaction between stakeholders and departments.
- Trade Secrets outline, what needs to protect in the supply chain. It can be in database list of the supplier, manufacturer, brand owner or store owners. It also includes employees data, email flow, process flow, etc.
- A detailed structure of involved stakeholders, teams, roles, hierarchy structure, user roles, daily interaction and flow of information and data needs to be planned before executing who, Does What, Reports to Whom, Where, When and How. Then teams can create proper roles and data packet they are generating in System.
- Data Packet Design for Blocks in the chain
- Data Block insertion rights, editing rights, and updates rights.
- Data Block planning, stage segregation systems, Flags from one status to another, highlighting blocks and confirmation of stage crossing.
- Blockchain Nodes for team stage crossing and coloring system with a satisfaction level.
- Consensus between team for crossing stage, creating orders, ETD and actionable buttons will be planned.
- Conflict Data Blocks inside the chain. They need to be highlighted in UI with actions to resolve by consensus with parties involved.
- Screen planning, Tree System planning, Stakeholders wise Access to blocks.
- Alert System configuration based on order, supplier, manufacturer, brands, stores, and shipping companies.
- Security of data and the entire system. We need to write all possible hacks, security threats, access control threats, data stealing within teams, consensus breaking and leakage by stakeholders.
- Planning for double confirmation and blocks, which need them. Generally, it will be used for stage crossing.
- Upgrades for the entire chain. In case of Upgrades, we need to plan for future with Data Blocks, Network, and Process flow.
Example of Data Blocks and Stages.
We are covering a small part of the chain. So we have a better idea chain shape and method. We have taken the process from brand ordering to manufacturer and manufacturing orders to suppliers.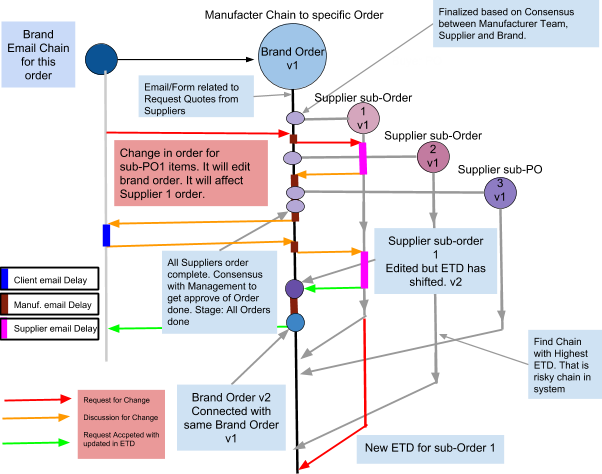
RFID Data in the same Blockchain
We are giving you an example from a Brand perspective. If Brand is giving an order to Manufacturer following data should be added in Blockchain for better tracking and following up with teams.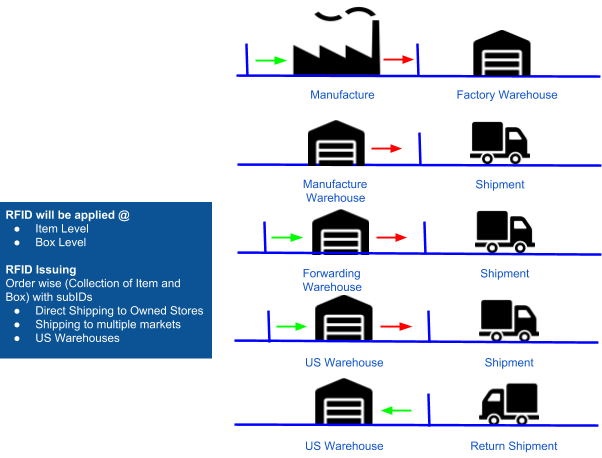
The small process explained for RFID implementation and data generation:
- Raw Material entry in Production
- Production started
- Finished Production in Factory
- Factory Shipped to Forwarding Warehouses
- Shipments
- Shipment to the destination in Direct
- Shipment to US Warehouses
- Received in US Warehouses
- Shipping to Client to Stores
- Return Shipment
The chain will be having all data blocks coming from RFID devices and stitched to the chain. This information will be provided with a timestamp in it.
Conclusion
We have to understand blockchain from philosophical level during planning and implementation. It is about companies opening up their data to other stakeholders for mutual benefits and automating processes. Many processes and orders are pending and waiting in the long supply chain due to approvals and confusions if we share that information with other stakeholders concerned with it. Then we can have accountability and streamline the process. There should be explicit consensus/agreement between quality, quantity and time between stakeholders in case of any editing in orders. It should be approved by both parties. It can reduce pressure from the supply chain.
“Information collected from various sources should be aligned for knowing one version of truth and transparency in the ecosystem without disturbing trade secrets of each stakeholder.”

